
下載億題庫APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360

下載億題庫APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360
請謹(jǐn)慎保管和記憶你的密碼,以免泄露和丟失

請謹(jǐn)慎保管和記憶你的密碼,以免泄露和丟失
Economies of Scale and Diseconomies of Scale
Economies of scale occur if, as the firm increases its output, cost per unit of production falls.
微信截圖_1596695908236420200806144732580.png)
微信截圖_1596677393945620200806144759673.png)
Diseconomies of scale occur if cost per unit rises as output increases.
微信截圖_159667740756520200806145833139.png)
Economies of scale can result from:
Increasing returns to scale.
Specialization economies.
Equipment and technology improvement.
Enhanced cost control and quality control.
More effective managerial decision making.
Bargaining power in input price.
Diseconomies of scale can result from:
Decreasing returns to scale.
Too large to be properly managed.
Overlapping and duplication products.
Higher prices because of supply constraints when buying inputs in large quantities.
微信截圖_1596677426190320200806150028253.png)
The minimum point on the LRAC curve is referred to as the minimum efficient scale.
The minimum efficient scale is the optimal firm size under perfect competition over the long run.
 900
900Portfolio Expected Return and Variance of Return:Return,RjFirst= 7.50 + 12.50 + 3.75 = 23.75.
 250
250Total, Average, and Marginal Product of Labor:Total,Average,Q:The aggregate sum of production for a firm during a time period. Usually:gathers the following information about the firm’s[PracticeMP = ΔTPΔL = 510 – 3203 – 2 = 1901 = 190.
 355
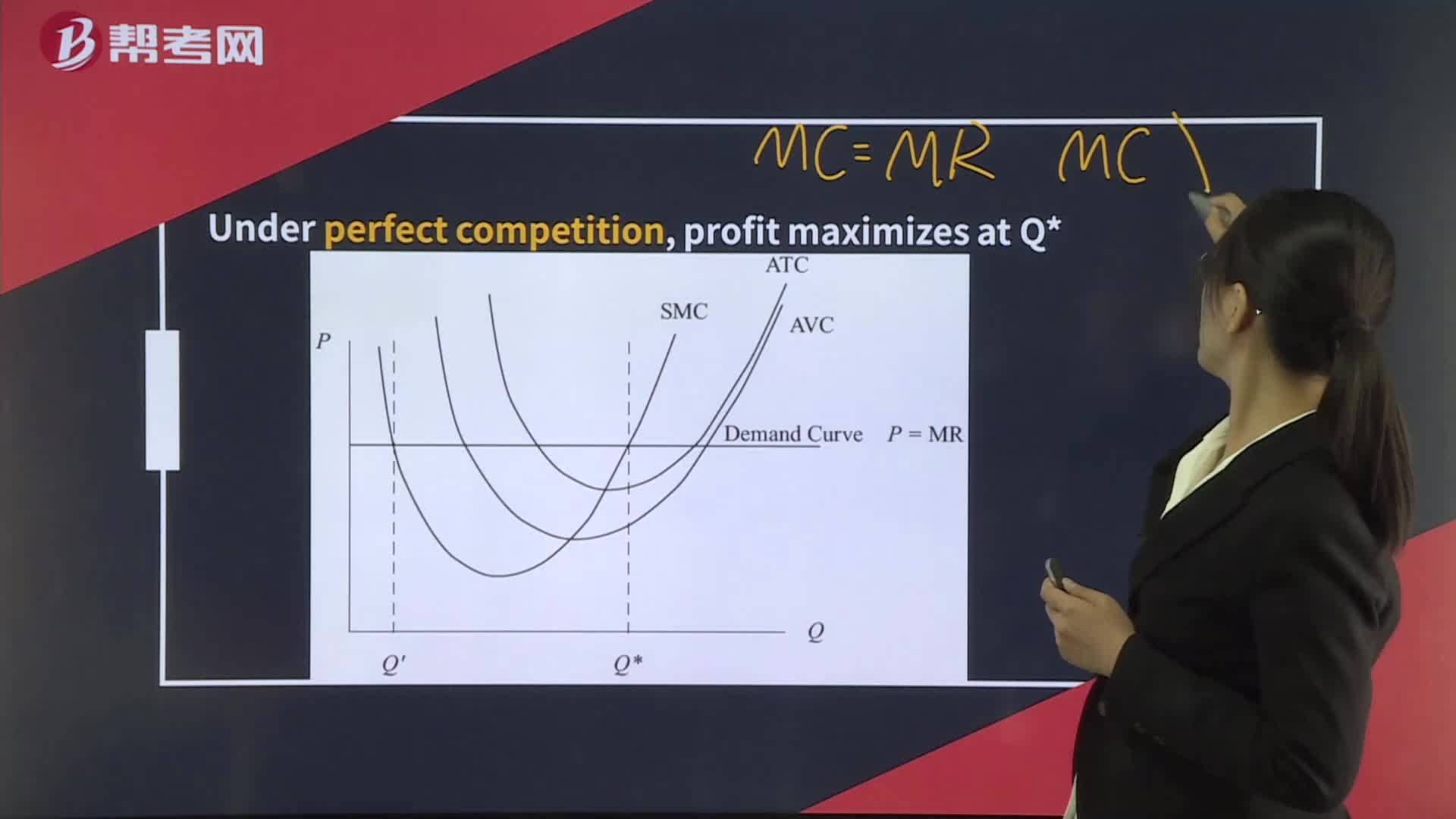
355Profit-Maximization, Breakeven, and Shutdown Points of Production:Points of Production:competition[Practiceminimized does not necessarily correspond to a profit maximum.

微信掃碼關(guān)注公眾號
獲取更多考試熱門資料