-

下載億題庫APP
-
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360

下載億題庫APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360
請謹(jǐn)慎保管和記憶你的密碼,以免泄露和丟失

請謹(jǐn)慎保管和記憶你的密碼,以免泄露和丟失
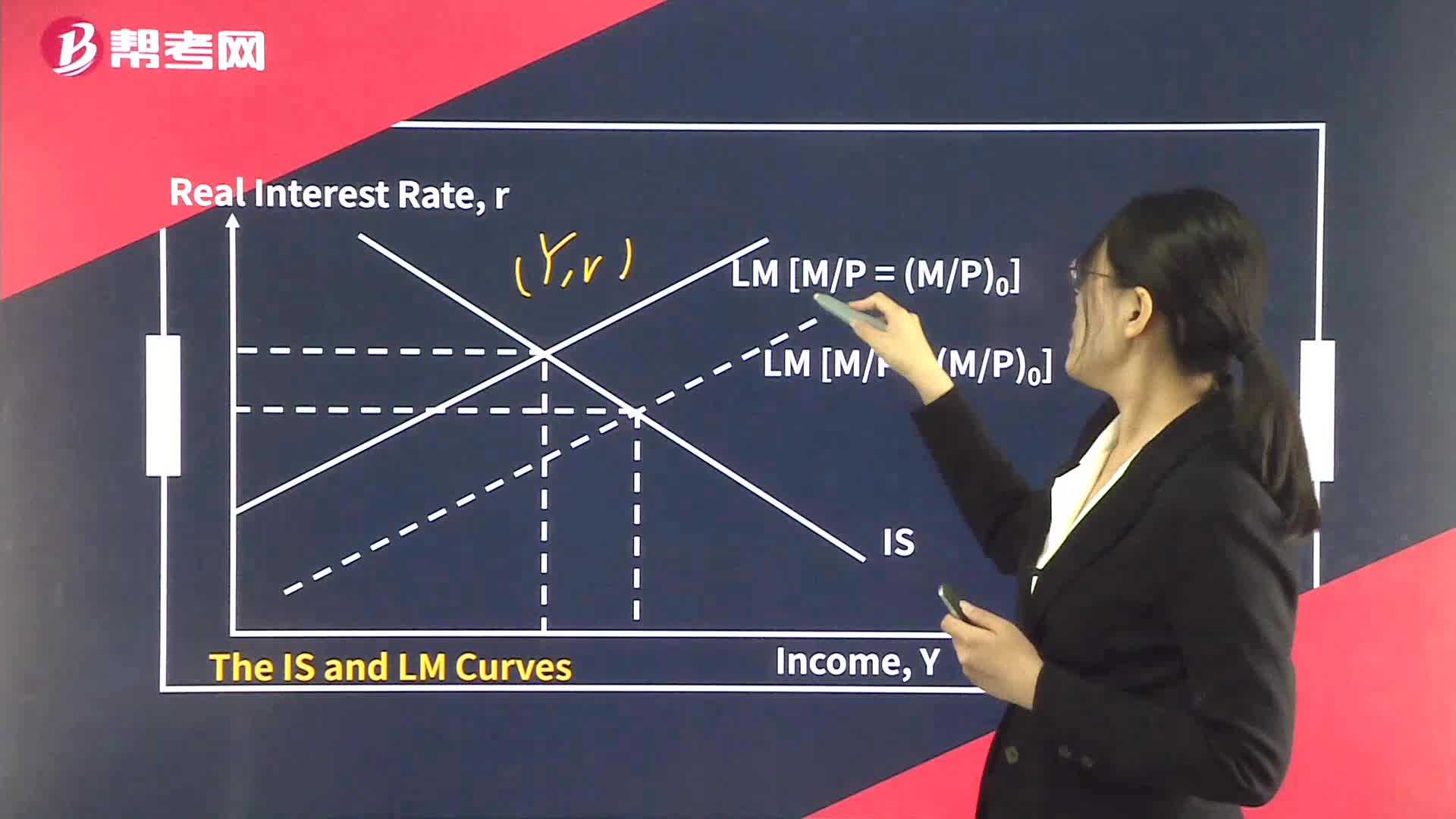
The LM Curve
The quantity theory of money equation
MV = PY
where
M is the nominal money supply;
V is the velocity of money, the average rate at which money circulates through the economy to facilitate expenditure;
P is the price level;
Y is real income/expenditure.
The supply and demand for real money balances:
M/P = (M/P)D = kY
where k = 1/V reflects how much money people want to hold for every currency unit of real income.
Demand for real money balances is an increasing function of real income and a decreasing function of the interest rate.
M/P = M(r,Y)
Given the real money supply (M/P), an increase in real income must be accompanied by an increase in the interest rate in order to keep the demand for real money balances equal to the supply. – The LM curve.
微信截圖_1596768966891420200807112322603.png)
 332
332
The LM Curve:MV = PY;where:Ybalances equal to the supply. – The LM curve.
 712
712
The IS Curve:where T = R – F denotes net taxes and S = SB + SH:GovernmentTotalinvestmentYNet
 354
354
The Aggregate Demand Curve:changes in private saving S.;money demand is insensitive to Y.
 08:39
08:39
2020-05-18
 04:30
04:30
 13:18
13:18
 13:11
13:11
 06:13
06:13
2020-05-15

微信掃碼關(guān)注公眾號
獲取更多考試熱門資料