Kinked Demand Curve in Oligopoly Market

Foreign Exchange Market Participants

Shifts in Aggregate Demand

Foreign Exchange Market - Spot Rates and Forward Rates

Identification of Market Structure – HHI

Identification of Market Structure – Concentration Ratio

Identification of Market Structure – Econometric Method

Shifts in Aggregate Demand and Supply

The Demand for Money

Factors Affecting Long-Run Equilibrium in Monopoly Markets

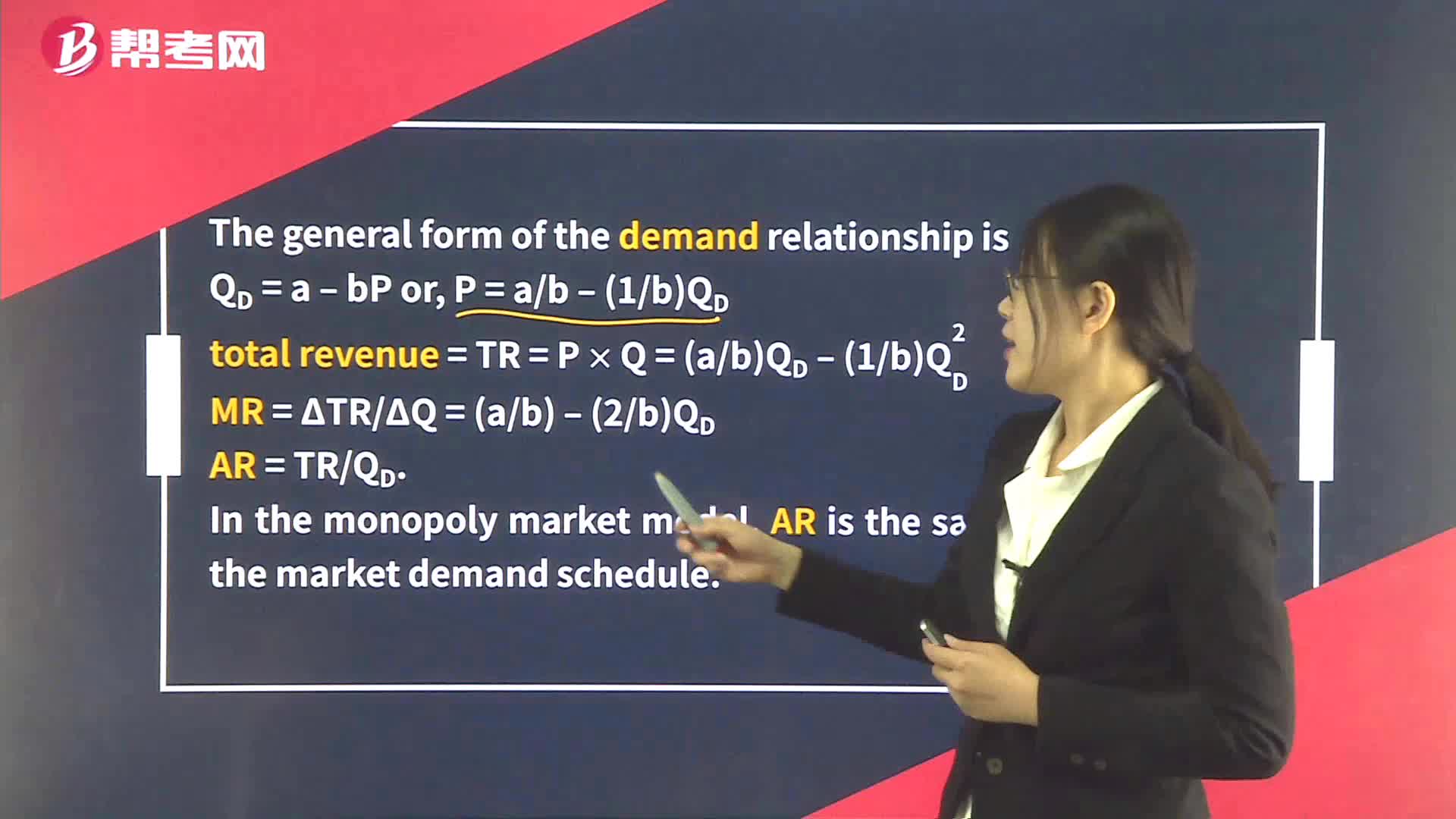
Demand Analysis in Perfect Competition

Demand Analysis:The Consumer

下載億題庫APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360