
下載億題庫(kù)APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360

下載億題庫(kù)APP
聯(lián)系電話:400-660-1360
請(qǐng)謹(jǐn)慎保管和記憶你的密碼,以免泄露和丟失

請(qǐng)謹(jǐn)慎保管和記憶你的密碼,以免泄露和丟失
Equilibrium GDP and Prices – Stagflation
Declines in aggregate supply bring about stagflation—high unemployment and increased inflation.
Increases in aggregate supply conversely give rise to high economic growth and low inflation.
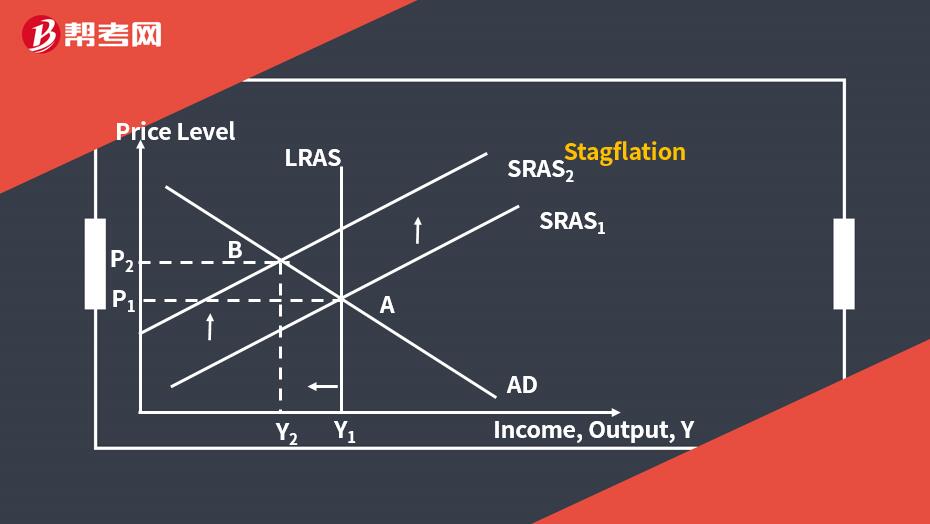
Higher costs for labor, raw materials, and energy lead to a decrease in AS, resulting in lower economic growth and higher prices.
Higher rates of productivity growth shift the AS to the right, resulting in higher output and lower unit input prices.
From an investment perspective, a decline in AS (leftward shift of the SRAS curve) suggests
reducing investment in fixed income;
reducing investment in most equity securities;
increasing investment in commodities or commodity-based companies.
 138
138Real GDP & Nominal GDP:Real GDP Nominal GDP:Real:PerGDPthe quantity of output available for consumption and investment.
 87
87GDP and GNP:quarter.,Gross,outside of the country.
 201
201Equilibrium GDP and Prices – Stagflation:and energy lead to a decrease in AS;increasing investment in commodities or commodity-based companies.

微信掃碼關(guān)注公眾號(hào)
獲取更多考試熱門資料